What is Two-Factor Authentication?
What is Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)?
Two-factor authentication (i.e. two-step authentication) is an additional level of security between your data and the outside world. This second layer of protection is there to provide peace of mind and ensure your passwords, financial information, personal data, and more are safeguarded from those with malicious intent.
How does 2FA work?
Two-factor authentication works by adding an additional login step to your account. This additional step is designed to inhibit those who have accessed your passwords from gaining access to any sensitive or personal information you have locked away.
Examples of two-factor authentication include receiving a phone call or text with a code, receiving an email with an authentication link, or having to retrieve saved secondary authentication codes. For obvious reasons, if your email or other devices are compromised, 2FA becomes irrelevant. However, this is rare.
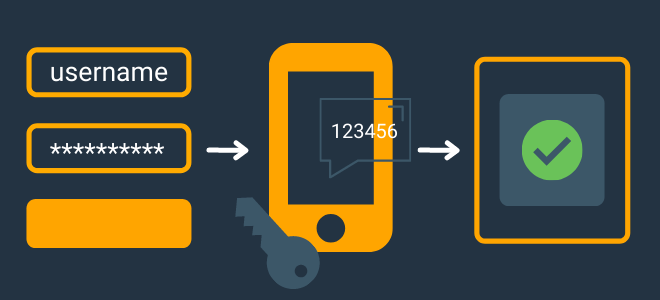
A graphic image depicting the process of two-factor authentication.
Some common 2FA types:
- A physical key (e.g. Titan Security Key): these are physical keys that are plugged into your computer when you require a two-factor authentication key.
- The Google Authenticator App: this is a personal favorite of ours. Simply install the app on your mobile device and tap the prompt on your device when signing into your accounts.
- Verification code: this is the most common form of 2FA. You receive a code or link via SMS (text), a call, or email. Personally, we find this verification method a bit slow and the message receipt can be inconsistent depending on your service connection.
The three basic authentication factors:
2FA is built on three things: something you know, something you have, or something you are. Below is a description of each:
- Something you know: this could be a memorized PIN code, the answer to a security question (e.g. the color of your first car), and your original password.
- Something you have: a physical object (e.g. a physical security key such as the Titan Security Key), an ID card, or your mobile device which acts as a secondary authenticator through either texts or calls, or authenticator apps like Google Authenticator.
- Something you are: this refers to biometric data such as Apple’s Touch ID or Face ID, or a retina scanner. Essentially, anything to prove that you are you!
Why passwords are no longer enough:
Passwords are easier to steal than ever. Many of us have been the victims of large data breaches where we hear through the news that Facebook, or Twitter, or HBO have had data breaches and millions of accounts have been compromised. 2FA provides an additional level of security so these breaches go from a potentially catastrophic event to a nuisance at best.
If your passwords are exposed to a hacker, 2FA means they can’t access your account.






[…] Two-factor authentication (2FA) is the most effective form of protection against phishing attacks. 2FA works by adding an additional step of protection for user login. […]
[…] deploy strong multi-factor authentication (MFA) to as many employees as possible. *Remember, some MFA can be circumvented–it is not a […]